How Does A Greenhouse Work? Detailed A-Z Guide
Ever wondered – “How does a greenhouse work?” Me too! That’s why I did some research and created this A-Z guide to save you the time and effort of figuring it out yourself.
Let’s get into it ☘️
Table Of Contents
How Does A Greenhouse Work – The Principles
The basic principle of a greenhouse is to trap and retain heat, converting sunlight into energy for the plants inside (1). Sunlight is essential for supporting photosynthesis and creating a warm environment within the structure.
If you’re someone that prefers to watch a video then here’s one below, otherwise keep reading:
Understanding the basic principle of a greenhouse
Greenhouses capture sunlight and convert it into energy, creating a warm environment to support plant growth year-round. They use transparent materials like glass or plastic to let in light while trapping heat, making them ideal for growing plants even in cooler climates.
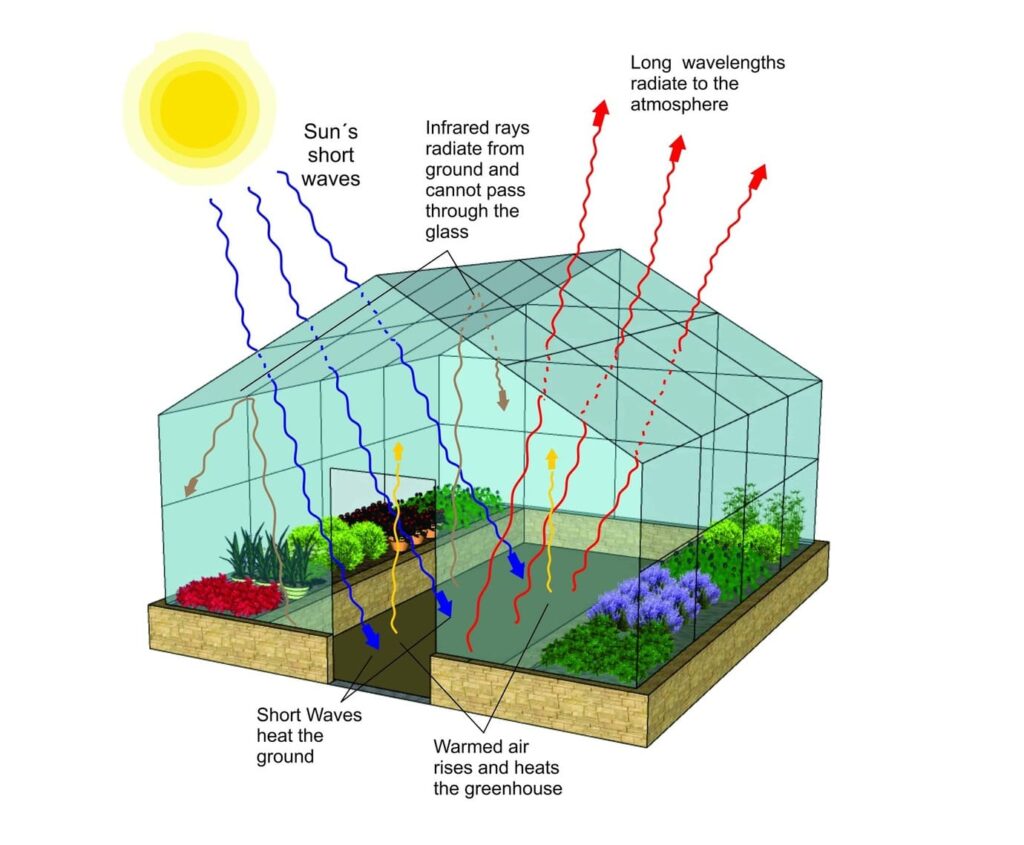
The short waves from the sun are able to penetrate through the greenhouse panels where they heat the ground and warm the greenhouse.
Then the long wavelengths that are emitted from the floor are able to radiate back out into the atmosphere while infrared waves are bounced around the structure heating the plants.
This trapped heat prevents cool air from affecting the plants inside, ensuring that temperature fluctuations outside do not impact the carefully maintained conditions within. Such settings are crucial for extending growing seasons, propagating specialized plant growth, and advancing modern agriculture techniques.
The role of sunlight
Sunlight plays a crucial part in the operation of greenhouses. It enters through transparent materials, like glass or plastic, which cover the structure. These materials allow light from the sun to penetrate inside, providing essential energy for plant growth.

This sunlight is then absorbed by plants and soil, kick-starting the process known as photosynthesis. Photosynthesis enables plants to create food from carbon dioxide and water using sunlight’s energy (but more on this in a little bit)
The heat generated by sunlight absorption warms the inside of the greenhouse. Unlike outdoor environments, this warmth doesn’t escape easily due to insulation provided by greenhouse building materials.
| As a result, greenhouses maintain a consistently warm environment that promotes specialized plant growth year-round. This controlled climate supports modern agriculture techniques by allowing crop production even in challenging weather conditions or off-season periods. |
Conversion of sunlight into energy
After understanding the significant role sunlight plays, it’s essential to delve into how greenhouses convert this sunlight into energy. Greenhouse materials are engineered to capture sunlight efficiently.
The transparent parts of a greenhouse, usually made from glass or specialized plastics, allow sunlight to enter while minimizing heat escape. This sunlight does more than just warm the interior space; it kickstarts a vital process for plant growth known as photosynthesis.
During photosynthesis, plants absorb sunlight using a pigment called chlorophyll. They use this solar energy to combine carbon dioxide from the air with water from the soil and create glucose, a type of sugar that plants use for food and growth.
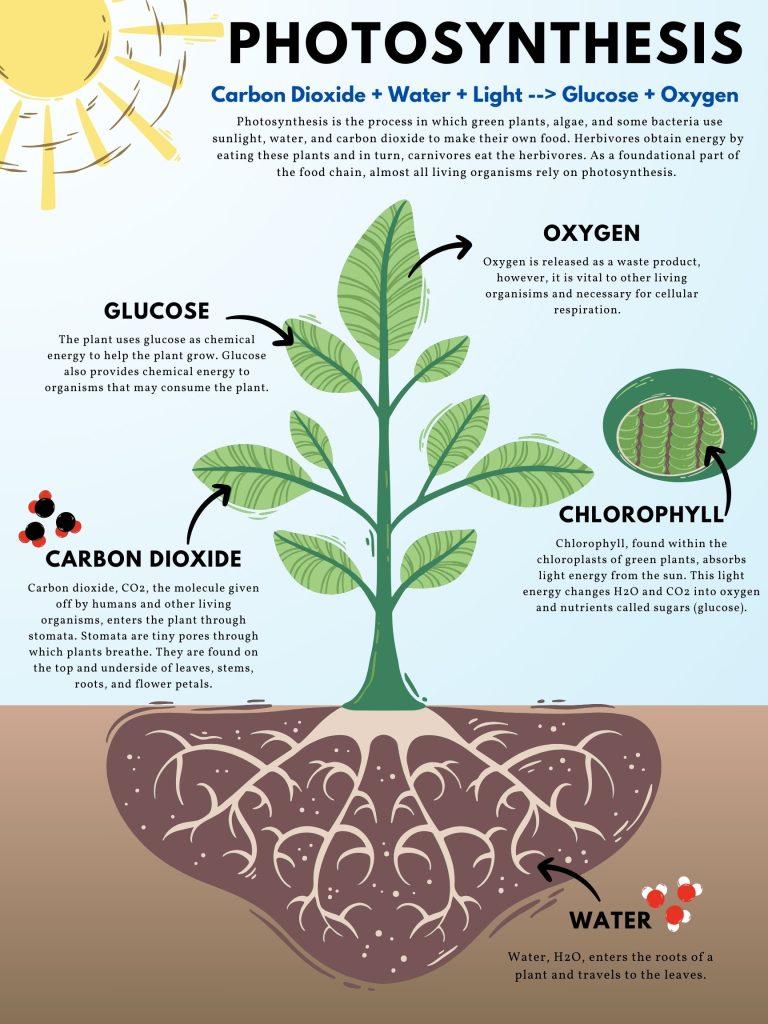
Oxygen is released as a by-product of this process, contributing to the atmospheric balance within the greenhouse. This conversion not only fuels plant development but also transforms the greenhouse into an ecosystem where air quality is continually improved through natural processes.
Trapping and retaining heat
Transitioning from the absorption of sunlight, retaining heat is essential for maintaining a warm environment in the greenhouse. Transparent materials like glass or plastic allow solar radiation to enter and trap infrared electromagnetic waves produced by plants and other objects inside the greenhouse.
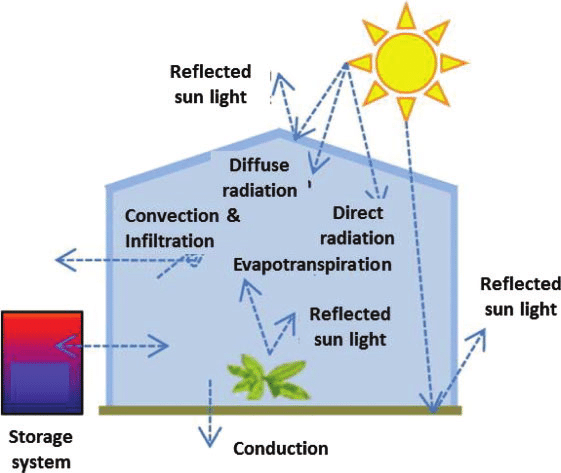
Retaining heat is fundamental for creating a favorable environment within the greenhouse.
How Does a Greenhouse Work: Summary
Here is a quick summary of how a greenhouse works through a series of steps:
| 1 – Incoming sunlight penetrates the transparent materials of the greenhouse, warming the interior. |
| 2 – The warmed surfaces inside emit infrared electromagnetic waves, retaining heat within the enclosed space. |
| 3 – This warm environment supports photosynthesis, crucial for plant growth and propagation. |
| 4 – Transparent building materials allow light to reach specialized plants, enabling year – round gardening and modern agriculture techniques. |
| 5 – Temperature control mechanisms help maintain optimal conditions for crop production and environmental control. |
| 6 – Proper ventilation techniques regulate humidity levels while promoting insulation and maintaining an ideal growing environment. |
| 7 – These elements work together to create a tailored atmosphere that underpins successful greenhouse farming, not only enhancing plant care but also maximizing crop production. |
Maintaining Optimal Conditions in a Greenhouse
Maintaining the ideal temperature is critical. Adequate ventilation techniques are essential for healthy plant growth in a greenhouse.
Temperature control
Maintaining optimal temperature levels within a greenhouse is crucial for creating an environment conducive to plant growth. This involves strategically managing the internal heat through insulation and ventilation techniques.
By utilizing transparent materials in the structure, the greenhouse maximizes sunlight absorption while minimizing heat loss. Additionally, controlling infrared electromagnetic waves inside creates a warm environment that supports year-round gardening and specialized plant growth.
Humidity is another factor to consider when regulating the greenhouse’s climate. Proper humidity control ensures ideal conditions for photosynthesis and plant propagation, which are essential for crop production and environmental control.
| Here are some of our favorite thermometers: 5 Smart Thermometers You Need In Your Greenhouse (2024) |
Ventilation techniques
Ventilation in a greenhouse is crucial for maintaining optimal conditions for plant growth. Simple techniques such as using roof vents, side vents, or exhaust fans can help regulate temperature and humidity levels.
The strategic placement of these openings allows for proper air circulation, preventing the buildup of excess heat and moisture while promoting healthy plant growth. Additionally, installing louvered windows can aid in controlling airflow by adjusting the angle to allow fresh air into the greenhouse.
These ventilation techniques play a key role in creating a well-balanced environment essential for successful greenhouse gardening.
Proper location and orientation
To ensure optimal performance, choosing the proper location and orientation for your greenhouse is crucial. Select a site that receives maximum sunlight throughout the day, as this is vital for plant growth.

Additionally, orient the structure north to south to allow for even distribution of sunlight and prevent shade from obstructing plant development. Proper positioning not only maximizes exposure to natural light but also aids in maintaining consistent temperatures within the greenhouse, creating an ideal environment for plants to thrive.
Tips for Maximizing the Benefits of a Greenhouse
Now that you know the answer to – “How does a greenhouse work in summer?” Let’s talk about how to maximize the benefits of a greenhouse, it’s crucial to select the best plants for optimal growth and yield. Utilizing the greenhouse effect and adopting expert advice on proper plant care and nutrition are key factors in achieving success.
Best plants to grow in a greenhouse
Tomatoes, cucumbers, and peppers thrive exceptionally well in a greenhouse environment. These warm-season vegetables benefit from the consistent warmth and protection offered by a greenhouse.

Additionally, leafy greens such as lettuce, spinach, and kale are ideal candidates for greenhouse cultivation due to their preference for cooler temperatures and controlled humidity levels.
Furthermore, herbs like basil, parsley, and cilantro flourish in greenhouses with ample sunlight exposure and well-regulated conditions.
The controlled environment within a greenhouse also encourages the growth of delicate plants such as orchids and ferns that require precise temperature regulation and higher humidity levels.
Expert advice and tips
To make the most of your greenhouse, choose plants that benefit from its controlled environment. Opt for heat-loving crops like tomatoes, cucumbers, and peppers. Consider using shade cloth during the hottest months to prevent overheating.
Position taller plants on the north side of your greenhouse to avoid shading smaller ones. Rotate crops regularly and keep an eye out for pests or diseases that thrive in warm, humid conditions.
Lastly, invest in a good-quality thermometer and hygrometer to monitor temperature and humidity levels closely.
Ensuring proper ventilation is crucial for a successful greenhouse garden. Circulating air prevents mold growth and helps regulate temperature while ensuring carbon dioxide distribution for photosynthesis.
Conclusion
Understanding the workings of a greenhouse is the key to harnessing its potential. The mechanisms, from sunlight absorption to heat retention, create an optimal environment for plant growth and year-round gardening.
With careful maintenance and thoughtful design, a greenhouse becomes a sanctuary for specialized plant growth and modern agricultural techniques. The art of greenhouse farming unveils secrets that lead to enhanced crop production and environmental control.

How Does A Greenhouse Work? FAQs
What is the purpose of a greenhouse?
A greenhouse is used to create an environment that supports plant growth by trapping heat and maintaining higher humidity levels.
How does temperature regulation work in a greenhouse?
Temperature inside a greenhouse is regulated through the greenhouse effect, where sunlight enters and warms the interior surfaces, creating a warmer environment for plants.
Can any plants be grown in a greenhouse?
Yes, various types of plants can be grown in a greenhouse, including flowers, vegetables, herbs, and even tropical plants that require specific climate conditions.
Do I need special skills to operate a greenhouse effectively?
Operating a greenhouse effectively requires basic knowledge of plant care such as watering, pest control, and monitoring environmental conditions like temperature and humidity.
How do pests and diseases affect plants in a greenhouse?
Pests and diseases can impact plants in a greenhouse due to the controlled environment which may encourage their growth; regular monitoring is essential for prevention and management.

References:
1 – Lauren Murphy, Samantha Allen – How Much Does a Greenhouse Cost?, taken from: https://www.forbes.com/home-improvement/outdoor-living/greenhouse-cost/




